The amount of vegetables you should eat daily varies according to age, gender, weight, height, and physical activity. However, most individuals require two to four cups of vegetables daily. (1) However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), just 10% of individuals regularly achieve these requirements. (2) Meeting veggie guidelines may be even more difficult for people watching their carbohydrate consumption, as certain favorite vegetables remain rich in carbohydrates. However, many vegetables are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, making them an excellent addition to low-carb diets.
There are several reasons why someone could choose a low-carb diet. Whether it’s for blood sugar control, weight reduction, or managing other metabolic problems, replacing high-carb vegetables with low-carb alternatives might be advantageous, especially when choosing high-fiber, low carb vegetables.
Some common vegetables are low in carbs yet high in fiber.
1. Cauliflower

Cauliflower is a popular vegetable for low-carb diets. It is a cruciferous vegetable that is low in calories and carbs but abundant in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It may be riced and used as a low-carb grain alternative or as a pizza crust for a low-carb twist on an old favorite.
One cup of cauliflower has 27 calories, 5 grams of carbs, and 2 grams of fiber. It also contains 51 milligrams (mg) of vitamin C per cup or 45% of the recommended daily amount. (3)
2. Broccoli
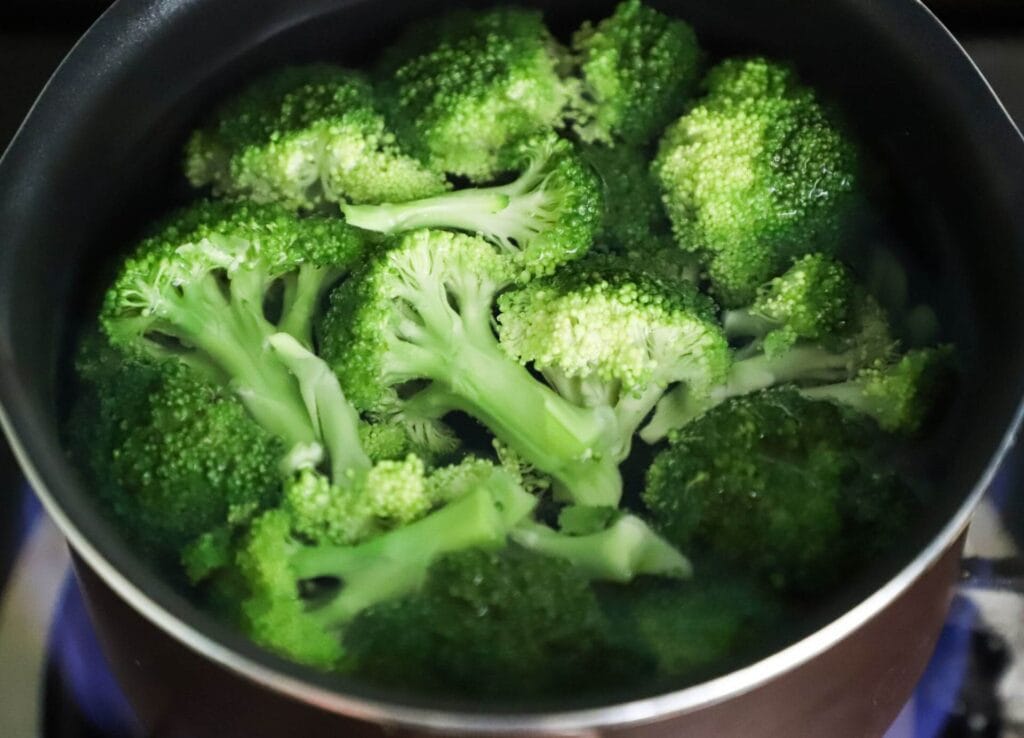

Broccoli, another cruciferous vegetable, has several vital elements despite its low carbohydrate content. One cup of broccoli has around 30 calories and 5 grams of carbohydrates. Each meal also contains around 2 g of fiber and vital vitamins and minerals such as folate, potassium, and vitamin C. (4)
3. Asparagus
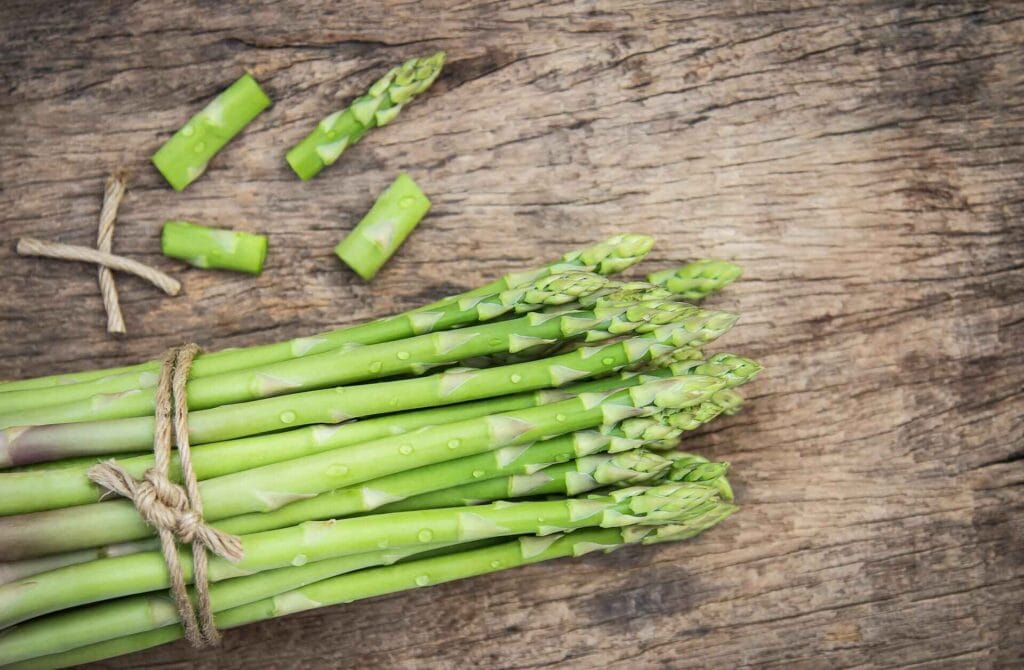

Asparagus comes in various hues, including green, purple, and white. It’s a favorite spring vegetable, but may also be consumed all year. While asparagus is often steamed or roasted, raw asparagus may offer a crunchy texture to cold dishes such as salads or sushi bowls.
One cup of raw asparagus has around 27 calories, grams of carbohydrates, and nearly 3 grams of fiber. It also contains enough vitamin K, vital for blood clotting, and folate, which is required for DNA synthesis. (5)
4. Purple Cabbage

Purple cabbage is another low-carb, high-fiber vegetable rich in minerals. Its purple color contributes various plant chemicals to a well-balanced diet. Purple cabbage has high levels of anthocyanin, a flavonoid that protects against oxidative stress-related disorders such as neurological and cardiovascular disease. (6)
One cup of purple cabbage has around 28 calories, 7 grams of carbohydrates, and 2 grams of fiber. Each meal also contains significant levels of vitamins C and K. (7)
5. Eggplant

The nightshade plant family includes eggplants, which are also known as aubergines. They are usually purple but can sometimes be crimson or black. Regardless of their hue, eggplants are nutrient-dense. One cup of eggplant has 21 calories, 5 grams of carbohydrates, and almost 2 grams of fiber. (8) Eggplants are abundant in antioxidants and critical vitamins and minerals. (9)
Eggplants are a versatile vegetable with a rich flavor and texture. It works well with various flavor combinations and may be roasted, sautéed, baked, or grilled.
6. Kale

Kale is very low in carbs and high in fiber. One cup of cooked kale has 60 calories, 6 grams of carbohydrates, and almost 6 grams of fiber. Kale is high in vitamins A, C, and calcium. (10) This leafy green can be eaten fresh as a salad or wrap or cooked as a savory dish.
7. Bell Peppers
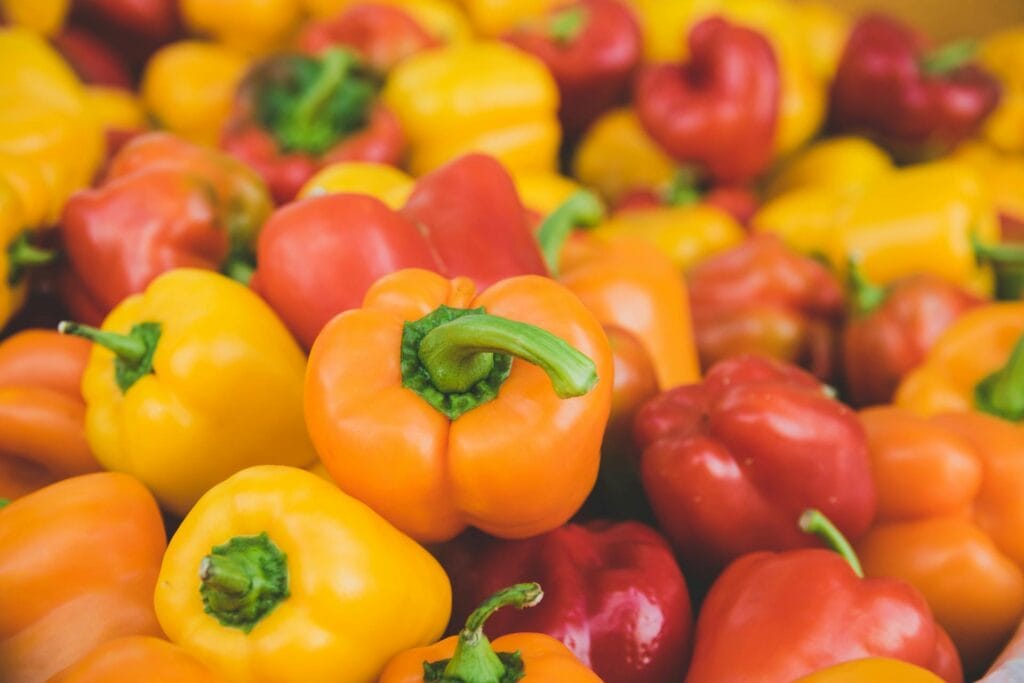

Bell peppers, also known as sweet peppers, are a healthy food with several advantages. They might be green, yellow, orange, or red, but all contain potent antioxidants that protect the body from oxidative damage.
One cup of chopped red bell pepper has 39 calories, 9 grams of carbohydrates, and 3 grams of fiber. It is also high in vitamins A and C, which are required for various biological activities. (11)
8. Mushrooms
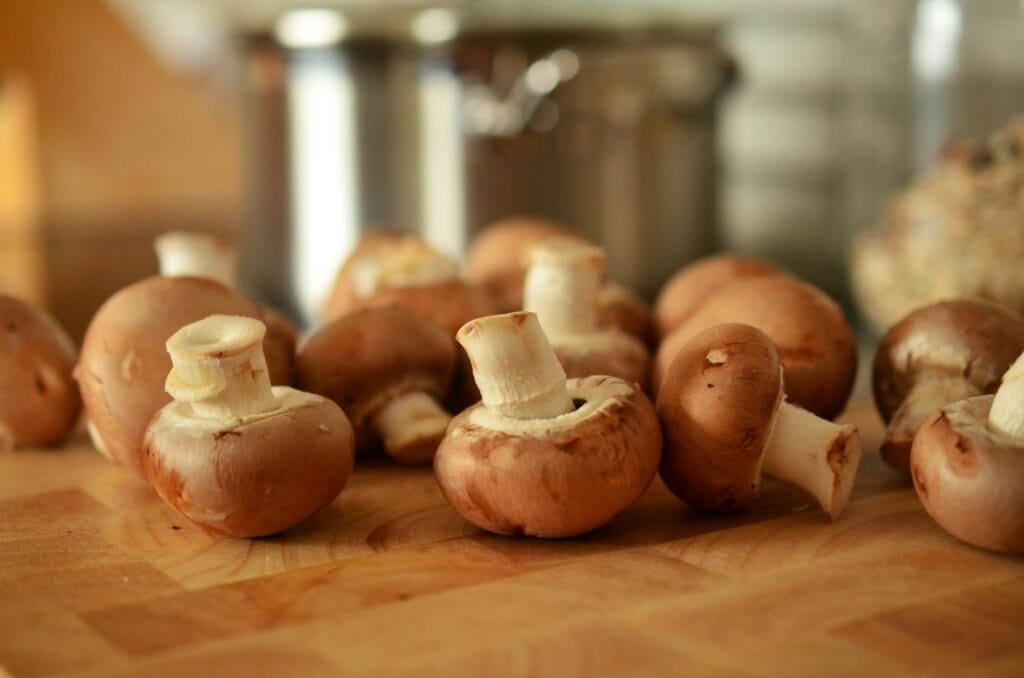

Mushrooms are very low in carbs. One cup has 15 calories, 2 grams of carbohydrates, and about 1 gram of fiber. (12) Mushrooms have been demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which can help improve metabolic indicators over time, such as blood sugar, cholesterol, blood pressure, and waist circumference. (13)
High-Carb Vegetables to Limit
Some veggies are higher in carbohydrate content than others, which can significantly influence blood glucose levels. If you’re on a low-carb diet, limit your intake of these veggies or consider replacing them with low-carb options.
Popular high-carb vegetables are:
- Potatoes: Potatoes are starchy vegetables with a high glycemic index, which means they can quickly raise blood sugar levels. (14) Instead of potatoes, try roasting low carb vegetables such as cauliflower or asparagus.
- Corn has a considerable quantity of carbohydrates (15). While it may be consumed moderately, others prefer chopped bell peppers or riced cauliflower alternatives.
- Peas: Green peas have more carbohydrates than their non-starchy relatives. (16) Leafy greens and bell peppers can supply equivalent nutrients while containing fewer carbs.
However, it is critical to remember that a good diet is about balance and satisfying individual nutritional requirements. A certified dietician can help you evaluate your specific nutritional needs and provide recommendations to help you satisfy them.
Why Are Low-Carb, High-Fiber Vegetables Good for You?
Increasing fiber while decreasing carbohydrate intake can have various health advantages. Adjusting the carb-fiber ratio can help control blood sugar levels, improve good digestion, lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, and aid in weight management.
According to the most recent Dietary Guidelines for Americans, individuals require 25-34 grams of fiber daily, depending on age and gender. Vegetables are a practical approach to boosting dietary fiber and satisfying these requirements. They are nutrient-dense, which means they have few calories but are high in vitamins and minerals.
Low-carb vegetables may provide nutrition and fiber to meals while avoiding an unpleasant blood sugar surge. Furthermore, fiber-rich veggies can boost satiety, keeping you filled for longer and lowering the risk of overeating.
Tips For Consuming Low Carb Vegetables
Low carb vegetables complement a well-balanced diet in various ways. Enjoy them cold as a refreshing snack, or use them in nutritious meals to boost nutrients and fiber.
Make a vegetarian omelet with bell peppers, tomatoes, and spinach for a colorful and healthy morning. Other selections include sweet potato hash with onions and bell peppers, egg muffins with spinach and feta cheese, and asparagus-stuffed salmon roll-ups.
Grilled veggie wraps with zucchini, eggplant, bell peppers, buttery quesadillas with sautéed mushrooms and spinach, and Caesar salads with kale are possible alternatives. You may also prepare stuffed bell peppers, eggplant lasagna, and mushroom risotto.
Low-carb veggies also make excellent snacks. Slice sweet potatoes, carrots, beets, and zucchini thinly and bake to make homemade veggie chips. Carrots dipped in hummus make a wholesome and pleasant snack. Enjoy a crisp, refreshing sushi roll by wrapping it with cucumber slices.
Individual dietary requirements and tastes will differ. However, a certified dietitian can help navigate the numerous alternatives available and ensure they satisfy predicted nutritional needs.
The Bottom Line: Low-Carb High-Fiber Vegetables Dietitians Recommend
Although a low carb diet is not suitable for everyone, some people may benefit from limiting their carbohydrate consumption. For example, persons at risk of acquiring type 2 diabetes, as well as those who are already treating the illness, must be cautious of the carbs taken at each meal and snack. Consuming low-carb vegetables will help you meet your carbohydrate targets while delivering critical nutrients.
Low-carb veggies, particularly those high in fiber, provide several health advantages. High-fiber, low carb vegetables have a lower influence on blood sugar levels while still offering several nutrients that enhance general health. Adequate fiber consumption can improve gastrointestinal health, regulate blood sugar levels, and lower the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.






0 Comments