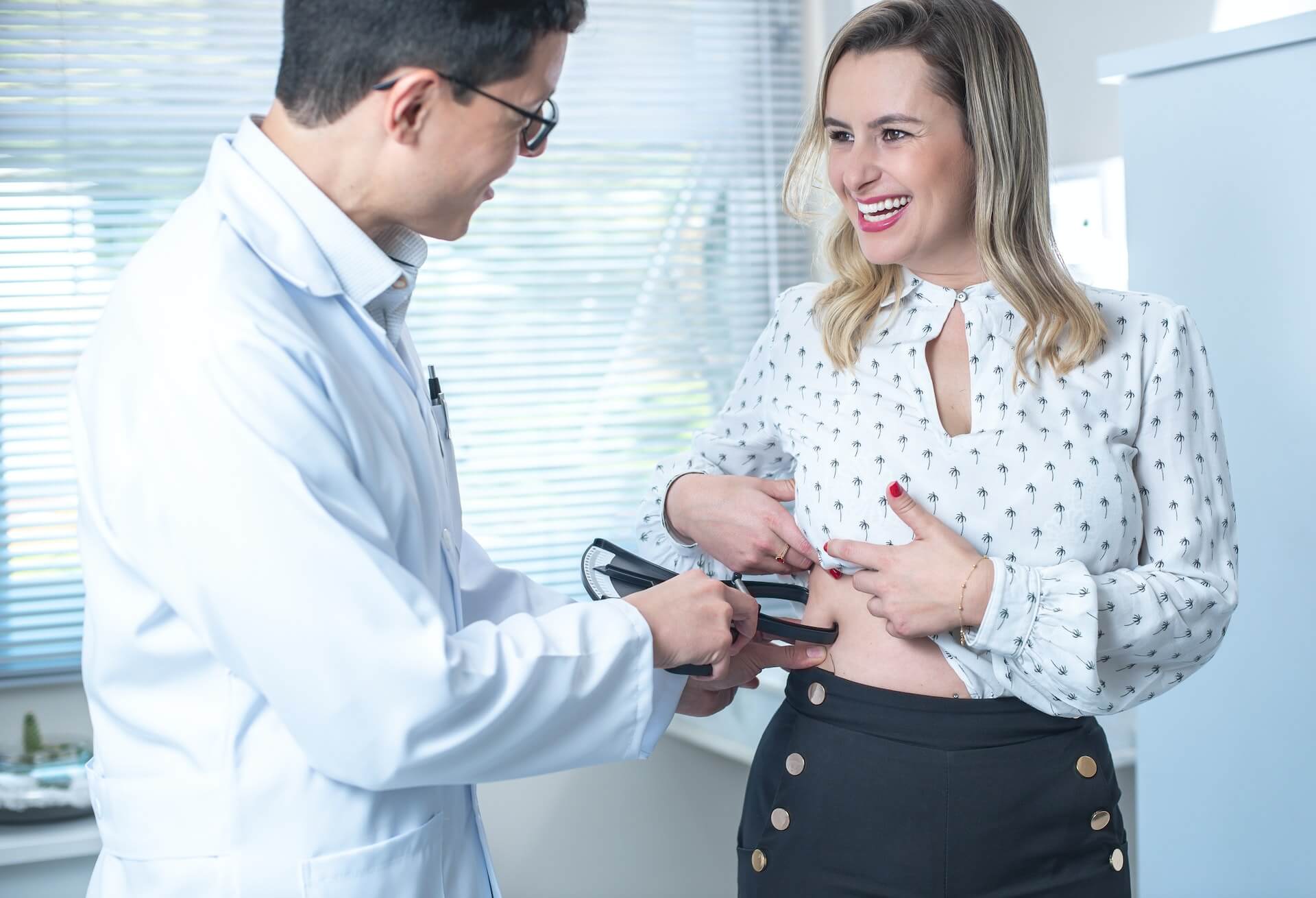
Why is belly fat a matter of worry, aside from personal appearance?
According to new research, the distribution of your body fat might predict your risk of heart disease and other disorders, and having a “spare tire” is worse than other forms of fat [1].
Indeed, if you carry fat around your stomach, you may be at a higher risk of health issues than overweight persons who store fat elsewhere — even if your body weight is “normal” [2].
Continue reading to find out why keto is the most effective method to burn fat, how belly fat causes health issues, and the most efficient techniques to decrease abdominal fat based on studies.

How Does a Ketogenic Diet Burn Fat?
In a nutshell, keto is the best fat-burning diet for the reasons listed below:
- Lowering your carbohydrate consumption lowers your insulin levels. Insulin limits fat burning on high-carb diets, while the keto diet’s reduced blood sugar and insulin levels make it simple to burn stored fat [3][4][5]. In some situations, keto-adapted people can burn up to ten times more fat than others [6].
- Without carbohydrates, keto causes your body to burn fat for fuel during activity and rest [7]. Fat-burning happens mostly during fasting (including overnight fasts) and exercise on other diet plans [8]. However, with keto, you may burn fat 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
- Ketones produced during ketosis naturally reduce appetite and cravings, resulting in a manageable calorie deficit [9][10]. The end outcome is long-term, sustained weight loss that does not need calorie tracking.
Following that, you’ll learn about the real-world fat loss consequences of adopting keto.
The Science Behind Keto and Weight Loss
The effects of keto on weight loss are not only theoretical.
There have now been hundreds of clinical investigations with thousands of volunteers to attest to its efficacy.
Here are some of the most important findings:
- A 2013 meta-analysis of 13 trials including 1415 people indicated that the keto diet resulted in higher long-term weight loss and improved health indicators compared to a low-fat diet [11].
- A 2012 research comparing a low-calorie with a low-carb, high-fat keto diet in type 2 diabetes patients revealed that the keto diet resulted in more significant reductions in body weight, waist circumference (belly fat), and blood glucose levels [12].
- A second 2012 research of 58 obese children aged 8 to 18 discovered that the keto diet resulted in higher decreases in body weight, fat mass, waist circumference, fasting insulin, and insulin resistance when compared to a low-calorie diet [13].
- An analysis of 12 studies on very-low-calorie keto diets (VLCKDs) in obese individuals published in 2020 reported an average weight loss of 10 to 15.6 kg (22-34.3 lb) and a waistline decrease of 12.6 cm (5 inches) [14]. The keto patients’ findings were steady for up to two years of follow-up, and 92.5% could keep to the diet.
The figures on waist circumference and belly fat are the most essential for our purposes in this paper. In the next section, you’ll learn why belly fat is the worst.
Why Belly Fat (Visceral Fat) Is Unhealthy
Being overweight or obese may raise the risk of major diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, some malignancies, and other conditions [15].
However, new research reveals that, at the individual level, body fat distribution is a far more reliable predictor of health risk [16].
In other words, where you store fat may be as significant as how much you keep.
And what if you’re overweight and have excess fat in the wrong places? That’s a significant issue for your health.
Here are some key concepts to comprehend this situation:
- Subcutaneous fat is a layer of adipose tissue (fat) immediately under the surface of your skin, located anywhere on your body. It is typical and healthy to have some subcutaneous fat. Even if you have this form of extra fat, it is the least problematic [17].
- Visceral fat is belly fat that forms within the abdominal cavity, around your stomach, liver, and intestines. It raises inflammatory levels in the body and causes health concerns, which is why visceral fat is dubbed “heart attack fat” [18].
- Ectopic fat: This fat forms in unexpected locations and is exceedingly unhealthy[19]. Excess fat accumulated in the liver, heart, or muscles (akin to the “marbling” seen in steak)[20] is are example. People who have more visceral fat are likely to have more ectopic fat elsewhere [21].
Differences in fat distribution may explain why some overweight persons are “metabolically healthy,” while others who aren’t overweight can have cardiovascular disease and other health issues because they have more “heart attack fat” [22][23][24][25].
Fortunately, there is a simple method for determining how much visceral fat you have and how it increases your risk of health problems.
A larger waist circumference is associated with more excellent visceral fat [26].
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), women with waist circumferences over 34.5 inches and males with waist circumferences over 40 inches are at a higher risk of heart disease and other problems [27].
According to some estimations, those with waist circumferences more significant than the cutoff figures have a double chance of dying from any cause [28].
The waist cutoff is lower for those who are “normal weight,” with a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 [29].
Normal-weight women’s waists should be 31.5 inches or less, while men’s waists should be less than 35 inches [30].
Unfortunately, most research on this problem has only included white people [31].
Some experts think waist measurements should be varied for persons of different ethnic groups [32].
A lower waist (and less visceral fat) is unquestionably better for your health, regardless of race.
7 Ways to Lose Belly Fat
#1: Eliminate Sugar and Reverse Insulin Resistance
Sugar, in addition to all of the other issues it causes, leads to visceral fat.
If you haven’t already, eliminating sugar from your diet is the most critical move you can take to prevent belly fat.
Fructose may be the root cause of rising belly fat levels [33].
According to the authors of a 2018 article, fructose causes cellular inflammation, which boosts cortisol levels and shifts stored fat from subcutaneous fat cells to visceral fat storage [34].
Sweetened drinks (such as sodas, which include high-fructose corn syrup) and table sugar (which contains 50% fructose) are the most prevalent sources of fructose [35].
Not by chance, research reveals that drinking sweetened drinks and eating sugary meals causes an increase in belly fat and ectopic fat [36][37].
Fruit sugar is less of a concern, even on keto, because fruits are real foods with low fructose, fiber, and natural antioxidants [38].
#2: Don’t Be Sedentary
Physical inactivity can increase belly fat, while frequent, modest exercise can have the opposite impact.
According to a 2018 study of nearly 3000 participants, sitting or watching television dramatically increased the chance of visceral fat storage [39].
The same study discovered that increased physical activity reduced the chance of having extra abdominal fat [40].
Similar findings have been seen in other studies [41][42].
To begin combating belly fat, you don’t have to transform from couch potato to athlete overnight. Walking every day appears to help reverse harmful belly obesity and improve body composition [43].
#3: Do Cardio
A cardio routine, avoiding sweets, and increasing physical activity may be the most crucial steps in decreasing belly fat.
Aerobic exercise is the most beneficial physical activity for lowering visceral fat levels, according to a 2012 comprehensive review [44].
In addition, a 2018 meta-analysis discovered that aerobic exercise substantially reduces belly fat in overweight people, even without calorie restriction [45].
What about HIIT (high-intensity interval training)?
So far, there is little evidence in favor of HIIT, although one study revealed that it was similarly effective as steady-state exercise and more time-efficient [46].
And according to a 2018 meta-analysis, “HIIT is a time-efficient strategy to decrease fat-mass deposits, including those of abdominal and visceral fat mass,” however, the optimum protocols have yet to be determined [47].
#4: Lift Weights
Weight training and other kinds of resistance exercise can also help you lose abdominal fat [48].
According to a 2012 analysis, athletic training may help retain muscle during aging, reduce inflammation, and change body fat distribution healthfully [49].
Although aerobic training takes less time, combining cardio and weights is the most effective approach to maintaining muscle mass, removing fat, and supporting healthy aging [50].
#5: Go Keto (Not Dirty Keto)
Keto is the most effective fat-burning diet for belly fat.
Research shows that the keto diet is more successful than other diets in reducing fat and lowering abdominal fat [51][52].
But, whatever you do, avoid the filthy keto method.
Dirty keto allows users to eat any cuisine that satisfies keto macros, which includes many bad options.
Consuming unhealthy processed meals, particularly those containing trans fats and other inflammatory components, increases visceral fat storage [53][54].
Instead, focus on nutrient-dense whole meals with abundant naturally occurring antioxidants [55][56]. Increasing your intake of omega-3 fatty acids may also aid in the reduction of inflammatory abdominal fat [57].
As a last option, you might dramatically reduce your calorie consumption on the keto diet.
Most people can achieve their weight reduction goals while on keto without monitoring calories.
VLCKDs, on the other hand, are supported by trustworthy research and can help decrease visceral fat [58].
If you pick the low-calorie, ultra-low-carb diet, ensure you’ve explored all other possibilities first. Also, use a VLCKD for a maximum of a few months, as a hunger state exists.
#6: Eat a High-Protein Diet
Eating enough high-quality protein is a tried-and-true technique for increasing metabolism, decreasing hunger, and igniting fat-burning [59].
A diet enriched in high-quality protein may also help avoid dangerous amounts of abdominal fat [60].
Protein consumption of 20% to 35% of total calories is optimal [61].
Consider adding keto-friendly whey protein post-workout if you’re also performing weight training to help burn abdominal fat.
According to a 2014 study, scheduling whey protein consumption around resistance training enhanced visceral fat reduction compared to protein alone or resistance exercise alone [62].
#7: Take MCT Oil
MCT oil and powder are one-of-a-kind keto supplements incredibly beneficial for fat loss.
A 2008 research, for example, discovered that patients on a weight loss plan who got 18-24 grams of MCT oil per day shed three times more fat over four months than those who received olive oil [63].
If you want to lose belly fat, MCTs are an excellent supplement.
A 2015 meta-analysis discovered that, compared to long-chain triglycerides (LCTS), MCTs significantly increased subcutaneous and visceral fat loss [64].
The Bottom Line: How ketosis burn belly fat
Extra abdominal fat is a serious health risk you cannot ignore.
It also indicates that it’s time to make some lifestyle modifications.
Some data shows that belly fat burns more quickly than other forms of fat–almost as if your body wants to get rid of it [65].
Following the advice in this article, you may lose unnecessary belly fat, lowering your risk of heart disease and improving your general health [66].






0 Comments