MCTs (medium-chain triglycerides) are a kind of fat present in various foods, including coconuts and dairy. Due to their unique health benefits, MCTs have recently garnered significant attention in the health and wellness sector. You may have noticed an increased use of coconut oil in cooking or MCT oil in coffee. But why does this unique fat enthrall so many individuals?
This article will explain what MCTs are, how they vary, the benefits of ingesting these fats, and how you may include them in your diet.
What are MCTs?
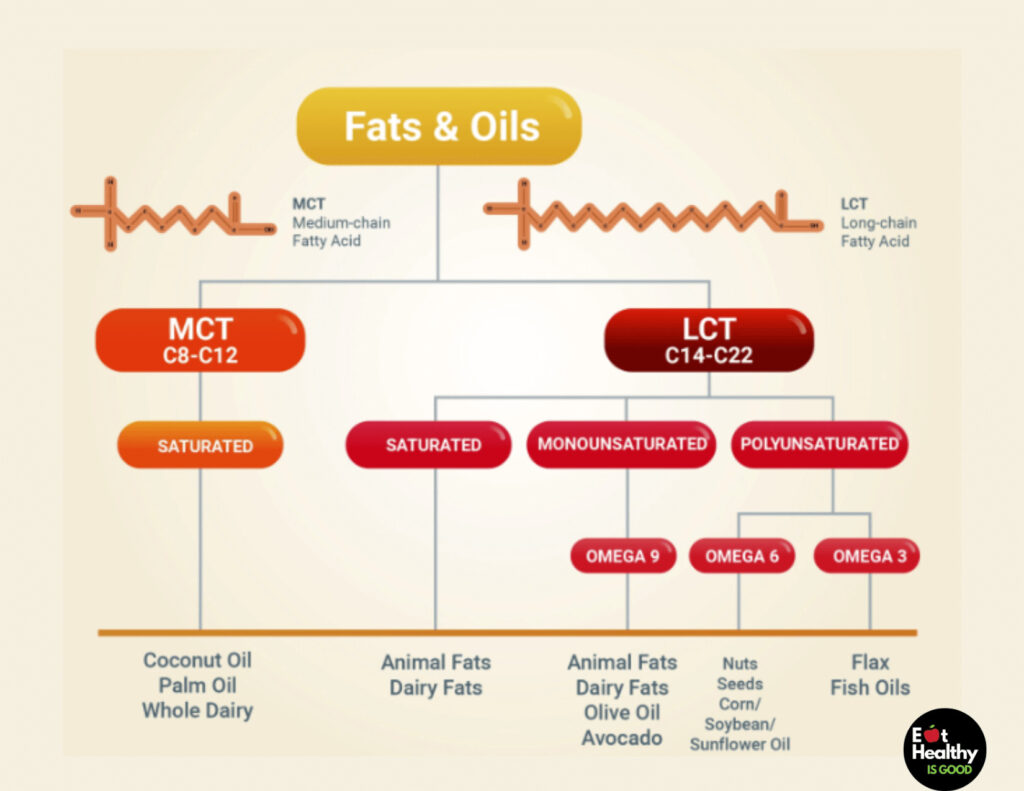
MCTs are saturated fats with distinct molecular properties that allow them to behave differently in the body than other fats. MCT is an abbreviation for medium-chain triglyceride, which refers to the carbon chain length in these fatty acids.
The number of carbons connected to a fat determines its classification. Long-chain triglycerides (LCTs) are lipids with 13 to 21 carbon atoms that make up most of our meals. MCTs, on the other hand, have a carbon chain length of 6 to 12 carbons. (1)
MCTs’ distinct properties are due to their medium carbon-chain length. Because fatty acids are digested by eliminating carbon atoms, the fewer carbon atoms a fat possesses, the faster it may be digested. This MCT property allows them to skip typical digestion and become an immediate energy source after ingestion.
MCTs are categorized into four different kinds of fats:
- C6 caproic acid
- C8 caprylic acid
- C10 capric acid
- C12 lauric acid
The length of each MCT affects its function since shorter MCTs degrade faster than longer MCTs. However, it is crucial to note that C6 has yet to be explored as fully as C8, C10, and C12.
Benefits of MCTs & MCT Oils/Powders
MCT oil usage has several advantages, the most significant of which are enhanced energy, antimicrobial properties, cognitive health benefits, and weight loss.
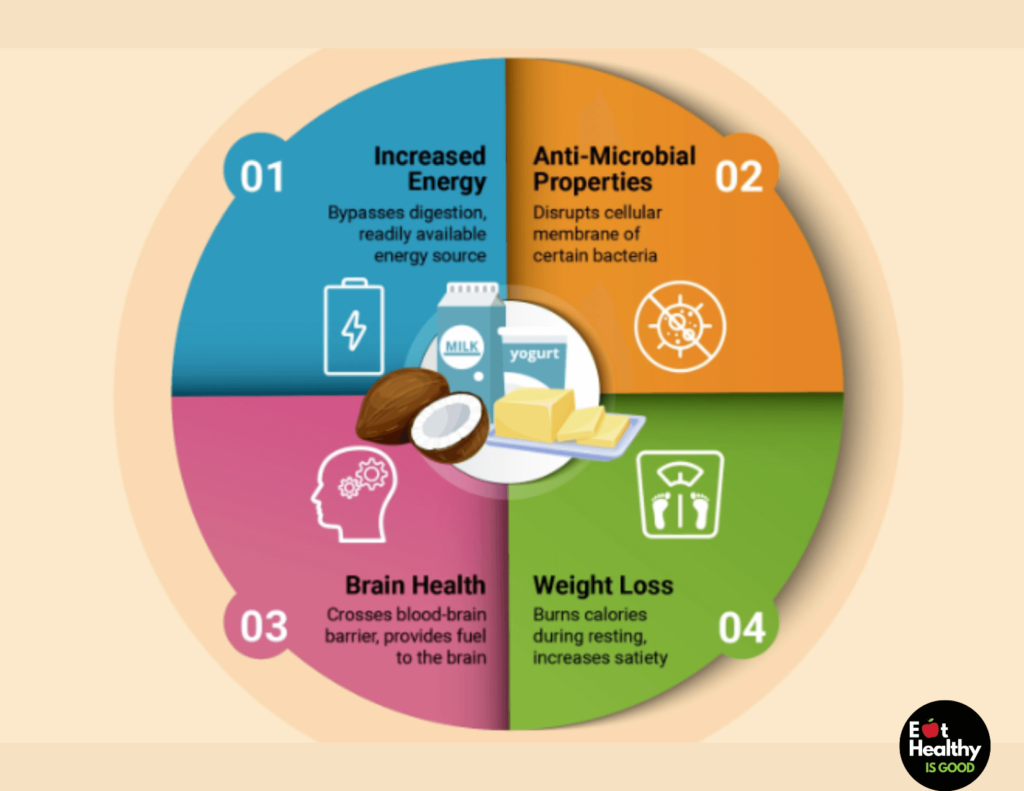
Increased Energy
Most of the research-backed advantages of MCTs are due to their quick digestion. MCTs are more rapidly accessible as an energy source after consumption because they skip typical digestion. This enables these fats to be utilized for ketone generation, making them the sole meal capable of doing so, and one of the reasons this fat is so popular on the ketogenic diet. According to the study, C8 may be the most efficient MCT for boosting ketone synthesis among the various MCT forms, followed by C10. (2)
It’s worth noting that C12, while formally classified as an MCT, also has LCT properties. This implies that C12 is not metabolized as rapidly as the other MCTs and hence has less effect on ketone levels.
Anti-Microbial Properties
While C12 may not be as efficient as other fats in promoting ketone generation, it does have robust anti-microbial characteristics, which means it can damage the cellular membrane of some bacteria, limiting further growth. (3) Because C12 is abundant in breast milk, it is considered to help create the groundwork for gut health in nursing newborns. While C8 and C10 have some antimicrobial characteristics, C12 has the most potent.
Brain Health
MCTs have also been linked to improved brain function. MCTs are quickly broken down by the body and turned into ketones by the liver. The ketones created can pass the blood-brain barrier and fuel the brain. (4) This improves cognitive performance, particularly in elderly or neurodegenerative persons, because as we age, our brain’s ability to consume glucose declines, and certain neurodegenerative disorders are characterized by reduced glucose consumption. (5) | (6) This is significant because, in these circumstances, ketones may fuel the brain when glucose cannot.
For example, in one research, six individuals with moderate cognitive impairment were given 56 grams of MCTs daily for 24 weeks. The findings supported MCTs’ potential to boost ketone synthesis, and the individuals’ memory improved compared to the control group. (7) This result has been bolstered by research on MCT intake in people with Alzheimer’s. (8)
Weight Loss
MCTs have also been linked to weight reduction. According to research, the unique digestion of MCTs leads the body to burn more calories during digestion, boosting resting energy expenditure. (9) While this is only a minor increase, burning more calories at rest can result in weight loss over time. Furthermore, the increased energy from MCT consumption might lead to increased activity and energy expenditure.
Finally, studies have indicated that MCTs promote satiety, most likely due to the ketones generated, helping people feel fuller for longer. (10) This can result in calorie restriction, which, combined with an increase in energy expenditure, is a formula for fat loss.
How do I consume MCTs?
MCTs naturally occur in coconut oil, palm kernel oil, butter, whole milk, and full-fat yogurt. However, the composition of MCTs differs depending on the source. Whole-food sources are high in C12 or lauric acid and low in the other MCTs. This implies that, while coconut oil is a terrific addition to your diet, using other MCTs will bring extra advantages.
MCTs are also isolated from whole food sources, most notably coconut and palm, to make an MCT oil composed mainly of C10. Compared to the food MCT sources indicated above, this MCT source has a far more vital capacity to boost ketone generation. MCT oil may be further broken down into oils with higher C8 or C6 content, allowing these oils to deliver stronger ketone-promoting benefits. MCT oil may be ingested in liquids such as coffee or dishes such as homemade keto-friendly salad dressings.
MCT Oil Side Effects
Because of its quick absorption, MCT oil can produce nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and upset stomach when eaten excessively by novices. As a result, it’s advised that you start with tiny serving sizes (about 5 to 7 grams or 1 teaspoon at a time) and check your tolerance before increasing the dose.
MCT Oil Powder
MCT oil powder is a recent product with the same advantages as MCT oil but with less stomach irritation. Spray-drying MCT oil and microencapsulating it with a “carrier” that permits it to enter powder form results in MCT oil powder. MCT powder is often easy on the stomach and dissolves more easily in drinks. MCT powder is growing more popular and is increasingly available in grocery shops and online.
When purchasing MCT oil powder, it is critical to consider the carrier source. Many items on the market will contain inexpensive fibers or even maltodextrin, which can cause blood sugar spikes and be detrimental to ketosis. For the most keto-friendly MCT oil powder, seek goods bonded to acacia fiber.
MCT oil powder is available in unflavored and flavored varieties, making it an excellent supplement to drinks such as shakes and smoothies. It’s also an ideal baking ingredient frequently used in keto sweets. Do you want to learn more about MCT oil powder? Check out our Perfect Keto’s Chocolate, Matcha, and Vanilla flavored MCT Oil Powders review.
The Bottom Line
MCTs are unique fats that the body breaks down differently, allowing them to deliver a variety of advantages. All four MCT forms have distinct advantages and are excellent additions to a healthy diet, particularly a ketogenic diet.
Start with a smaller portion amount if you’re new to MCT oil and gradually increase as tolerated. Remember that whole-food MCT sources, such as coconut oil, have distinct advantages over MCT oil supplements, so you may want to include both in your diet for the greatest results.




![How Low Carb and Ketogenic Diets Boost Brain Health [Benefits & Effects]](https://eathealthyisgood.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/pexels-ella-olsson-1640773-1-1080x675.jpg)


0 Comments